INTERVIEW
QUALITATIVE | TRADITIONAL | EXPLORATORY | GENERATIVE | SELF REPORTING
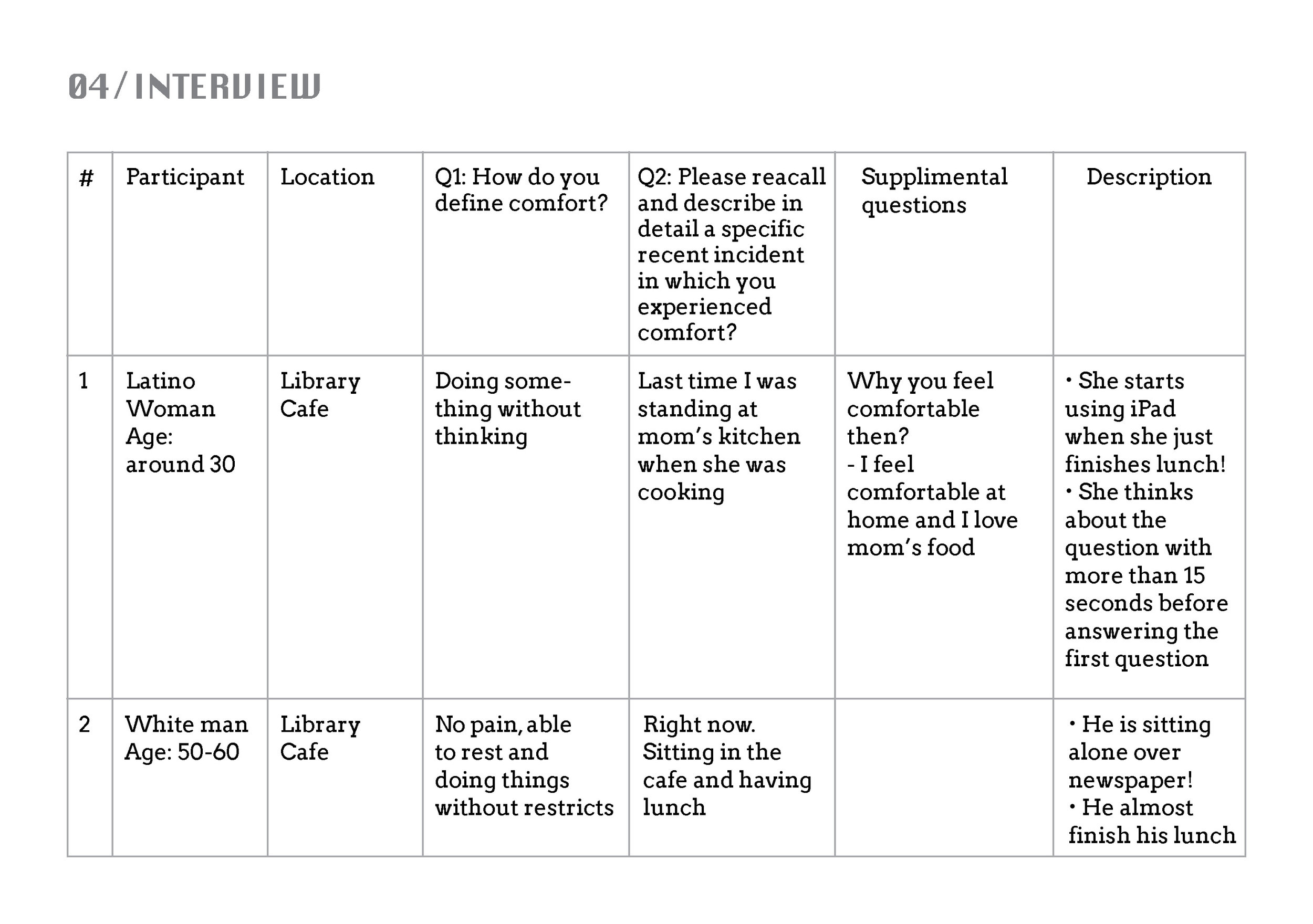
Interview is a direct way to contact with your subjects by inquiring specific questions about certain topics.
01 Definition
Interviews are a fundamental research method for direct contact with participants, to collect firsthand personal accounts of experience, opinios, attitudes, and perceptions.
---- Universal Methods of Design
An interview is a conversation between two or more people where questions are asked by the interviewer to elicit facts or statements from the interviewee. Interviews are a standard part of journalism and media reporting, but are also employed in many other situations, including qualitative research.
---- Wikipedia
02 NATURES
Notes:
- Combining interviews with other techniques - such as observation look at behavior, listen to perceptions --- Miller and Crabtree, 1999
- actors - people - demographic; activities - behaviors; time - duration, begin-middle-end; place - location and place
- recording talk: what they say - time + get context when you do analyze, relation matters(what reminds me) interpreter write down - the thing out of the expectation
Suited Context:
- Initial exploration: asking these broader questions in an interview or focus group can help you generate a deeper and more nuanced understanding of the problem.
- Requirements gathering: Interviewing in search of requirements requires an appropriately broad and opened view of the possibilities.
03 PROCEDURES
- Identify the place - where
- Identify the objective/ group of objectives - who
- Decide interview strategies - how? fully structured/ semi-structured/ unstratructed?
- Form? Face-to-face? telephone? E-mail? Message?
- Types of question closed?open-ended?complete a sentence? conceptual mapping?
- Practice to run through the process
- Prepare a clear and concise guide - remeber which steps to take and when to take
- Have appropriate back-up plans
- Check the recording devices
- Observe non-verbal cues or concers when taking notes
- Record the time and get context related to any idea
- To maximize the value of records, make data analysis on site
04 REFLECTION
Limitation
- Labor-intensive potentially unbounded discussions
- It requires researcher listening, taking notes, decide the further questions, understand non-verbal reactions higher effort requirement
- limited interview - based studies analysis - transforming raw notes and recordings of open-ended responses to broad questions.
Strengths
- It ables to go deep within the session
- Researchers could get open-ended and exploratory information
- Opportunistic interviewing - taking an interesting idea and running with it
- It won't cost money and time, so it is an effective way to collect data
05 Case Document